Synthetic
Synthetic base oils are manmade by chemically synthesizing compounds to produce a specific molecular structure. Typically, synthetic base oils are derived from petrochemicals or other feedstocks
Structure
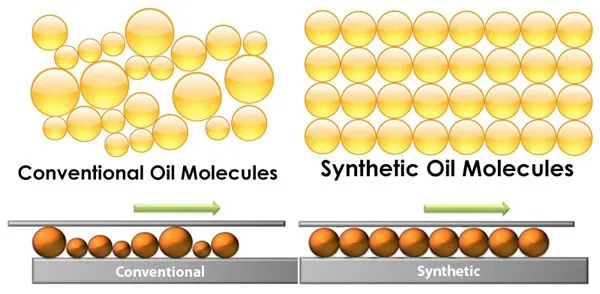
Synthetic base oils have a uniform and consistent molecular structure. They are engineered to have specific properties by altering the molecular structure for desired characteristics.
Performance
Synthetic lubricants are manufactured to have higher levels of purity compared to non-synthetics and can be formulated to have consistent properties Synthetic lubricants offer superior performance over non-synthetics and are exceptionally advantageous in high temperature or extreme pressure applications.
Non-Synthetic
Non-Synthetic or Mineral base oils are derived naturally from crude oil put through a refining process. They are a complex mix of hydrocarbons and impurities like sulfur, nitrogen and oxygen compounds.
Structure
Mineral base oils have a complex and irregular molecular structure, comprised of hydrocarbon chains and branching cyclic structures.
Performance
While synthetic oils may outperform traditional non-synthetic lubricants, many mineral base oils are less expensive and require a less specialized manufacturing process. Overall, non-synthetic lubricants provide moderate performance compares to synthetics. This is due to a lower viscosity index which can cause lubricants to thin out and a much lower range of thermal stability, excluding it from high or low-temperature applications.
Benefits of Synthetic over Non-Synthetics:
- Less friction
- Higher oxidation resistance
- Higher chemical resistance
- Higher thermal stability
- Lower toxicity
- Lower volatility
- Higher viscosity index
- Lower pour point
- Longer oil life
- Reduced oil consumption
- Higher flash point

